Exercise Is Good For Your Brain
03/05/2012 Leave a comment
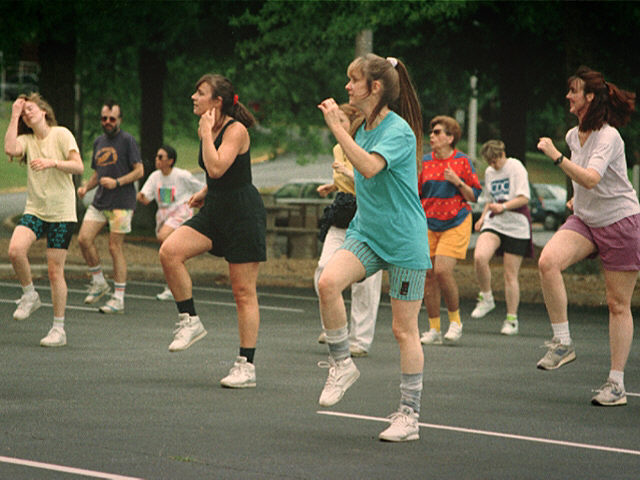 |
| Photo Credit: PD-USGOV |
Revitalize Your Life: Fitness, Nutrition, Weight Loss, Holistic Health.
03/05/2012 Leave a comment
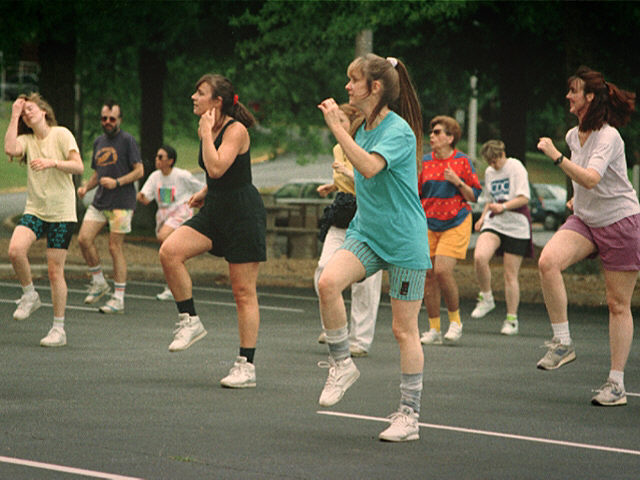 |
| Photo Credit: PD-USGOV |
03/04/2012 Leave a comment
 |
| Photo Credit: Kristopher S. Wilson Public Domain |
02/26/2012 Leave a comment
 |
| Photo Credit: Public Domain |
Do not ignore depression. Sometimes even exercise and healthy diet cannot alleviate feelings of depression. Moderate to severe depression may require immediate medical intervention. If you or a loved one could be suffering from depression, seek help.
For more information about depression and depression help resources, see:

02/06/2012 Leave a comment
 |
| Photo Credit: GiryaGirl CC-BY-SA-3.0 2011 |
For more information and kettlebell exercises, see:
01/27/2012 Leave a comment
 |
| Photo Credit: FEMA Public Domain |
Most Americans do not get enough exercise. Inactivity and an unhealthy diet can lead to obesity, heart disease and diabetes. Exercise can help reduce weight and lessen the risk for heart disease and diabetes. You can lose weight by cutting back on calories, but to prevent regaining lost weight, exercise is essential. You don’t have to join a gym or buy expensive equipment to exercise and lose weight for a healthy heart. But if you have been inactive for years, or if you don’t know how to begin, see your doctor for a check-up and consider a personal trainer to help you develop an exercise program that will work for you.
You can get more exercise during the day than you realize. You can maximize the aerobic value of your everyday activities. People with babies and small children often take a stroller along when shopping or going to the park. Pushing your child in a stroller for 1/2 hour or about 1 1/2 miles is excellent aerobic exercise for you and fun for your baby. As you begin to lose weight and feel stronger, consider buying a jogging stroller for your child. You can push baby along while you jog through the park. Walk the dog for an extra 10 minutes each day. Your dog will love it and you will get more exercise. Mowing the lawn and raking leaves are common activities that are good exercise for weight loss and a healthy heart. Use a push mower to cut your grass. Shoveling snow is also good exercise, but be careful not to over-exert yourself during cold weather. Limit shoveling to no more than 15 minutes and then rest for 15 to 20 minutes. Park your car a few blocks from your workplace and walk when weather permits. Walking is one of the safest and easiest heart healthy exercises. Walk instead of driving when you can. Take the stairs instead of the elevator or escalator.
Set aside at least 30 minutes every other day just for exercise. If you don’t know how to begin, a fitness trainer can help you develop an exercise program that works with your schedule and your current level of fitness. You can break up your 30 minutes of exercise into 10 minute blocks of exercise spread throughout the day. Exercise is a critical part of a healthy life. Keep your heart strong and lose weight by eating a nutritious diet and exercising.
01/20/2012 Leave a comment
 |
| Photo Credit: Beach Cruiser CC-BY-2.0 2009 |